FORCE's eXamining the Relevance of Articles for You (XRAY) program looks behind the headlines of cancer news to help you understand what the research means for you.
XRAY is a reliable source of hereditary cancer research-related news and information.
Learn more about the XRAY program
Categories Cancer Risk
Relevance: High


Strength of Science: High


Research Timeline: Post Approval


Study : Daily high-dose aspirin taken for at least 2 years reduces the risk of colorectal cancer but not other cancers in people with Lynch syndrome
Relevance: High


Strength of Science: High


Research Timeline: Post Approval


Most relevant for: People with Lynch syndrome
Research has shown that daily aspirin use can reduce the risk of colon and other cancers. The Cancer Prevention Program 2 (CaPP2) study looked at the effect of daily aspirin in patients with Lynch syndrome. After 10 years of follow-up, the results showed that taking daily aspirin for two years reduced the frequency of colon cancer in patients with Lynch syndrome, and importantly, did not result in an increase in side-effects or complications. No benefit was seen for other Lynch syndrome-related cancers, including endometrial cancer. (5/17/21)
Este artículo está disponible en español.
Read More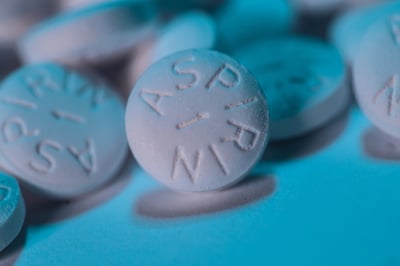
Update : Cancer disparities: Colorectal cancer in African Americans
Most relevant for: African Americans concerned about colorectal cancer
The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) released a 2020 report about cancer disparities among racial and ethnic groups in the United States. In this XRAY review, we highlight data from the report about the burden of colorectal cancer in African Americans, who have the highest rates of diagnosis and death related to the disease among all racial and ethnic groups. (Posted 4/27/21)
Este artículo está disponible en español.
Read More
Relevance: Medium-High


Strength of Science: Medium-High


Research Timeline: Post Approval


Study : Body Mass Index (BMI) may affect how well aspirin use protects against colorectal and ovarian cancer
Relevance: Medium-High


Strength of Science: Medium-High


Research Timeline: Post Approval


Most relevant for: People concerned about their risk of colorectal or ovarian cancer.
This study looked at the impact of daily aspirin use on the risk for many types of cancers and whether this effect can be modified by risk factors such as obesity, smoking, physical inactivity or a family history of cancer. Daily aspirin use:
- lowered the risk for colorectal cancer, but this effect was lost as Body Mass Index (BMI) increased.
- lowered the risk of ovarian cancer risk among obese women.
- offered little or no protection against breast, endometrial or advanced prostate cancer.
(posted 3/19/21)
Este artículo está disponible en español.
Read More
Relevance: Medium-High


Strength of Science: Medium-High


Research Timeline: Human Research


Study : Breastfeeding may lower risk of ovarian cancer in women with BRCA mutations
Relevance: Medium-High


Strength of Science: Medium-High


Research Timeline: Human Research


Most relevant for: Women considering breastfeeding who have inherited BRCA mutations.
Data from a large-scale study suggests that breastfeeding may protect against ovarian cancer in women with inherited mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2. (1/28/21)
Este artículo está disponible en español.
Read More
Update : FDA approves new imaging drug for detecting spread of prostate cancer
Most relevant for: Men with prostate cancer
On December 1, 2020 the FDA approved a new type of imaging technology to confirm the spread of newly diagnosed prostate cancer that is suspected to be metastatic. The approval also includes use for confirming suspected recurrence in men who have rising PSA after treatment. The approval is based on two clinical trials that showed this new technique to be safe and consistent in accurately detecting cancer that has spread beyond the prostate gland. (1/7/21)
THIS INFORMATION HAS BEEN UPDATED on 5/10/2022: On March 23, 2022 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a new drug called Pluvicto to treat patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. ON the same day, the FDA also approved a new imaging drug called Locametz (a brand of Gallium 68 PSMA-11) for identification of those patients who would benefit from treatment with Pluvicto. Read about the FDA approval of Pluvicto and Locametz here.
Este artículo está disponible en español.
Read More
Relevance: Medium-High


Strength of Science: Medium-High


Research Timeline: Human Research


Study : Women support delayed removal of ovaries
Relevance: Medium-High


Strength of Science: Medium-High


Research Timeline: Human Research


Most relevant for: Women at high risk of ovarian cancer who are considering undergoing risk-reducing surgery.
Risk-reducing early removal of fallopian tubes followed by removal of ovaries at a later date was acceptable to women at high risk of ovarian cancer due to an inherited mutation in a recent study. This was especially true for women worried about sexual dysfunction associated with surgical menopause. (12/24/20)
Read More
Relevance: Medium


Strength of Science: Medium


Research Timeline: Post Approval


Study : Inherited gene mutations found in pancreatic cancer families in Spain
Relevance: Medium


Strength of Science: Medium


Research Timeline: Post Approval


Most relevant for: People with pancreatic cancer and a family history of pancreatic or other cancers
This study looked for inherited mutations in genes known to be linked to hereditary pancreatic cancer. The results provide additional evidence that most hereditary pancreatic cancer is due to inherited mutations in genes that were previously associated with other forms of cancer. (10/29/20)
Read More
Relevance: Medium-High


Strength of Science: Medium-High


Research Timeline: Post Approval


Study : Knowing about an inherited BRCA mutation improves outcomes for women with breast cancer
Relevance: Medium-High


Strength of Science: Medium-High


Research Timeline: Post Approval


Most relevant for: Young women with, or at high risk for an inherited BRCA mutation
Inherited mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are linked to a high lifetime risk of breast and other cancers. This study shows that women who know that they have a BRCA mutation before they are diagnosed with breast cancer have improved outcomes including diagnosis at earlier stages and improved overall survival. (10/26/20)
Read More
Relevance: Medium-Low


Strength of Science: Medium-Low


Research Timeline: Human Research


Study : Dairy milk may slightly raise breast cancer risk
Relevance: Medium-Low


Strength of Science: Medium-Low


Research Timeline: Human Research


Most relevant for: Women who consume dairy or soy
Debate continues about whether consuming soy or dairy products increases breast cancer risk. This study looked at a large number of women and found no link between soy and breast cancer risk. The study did find that postmenopausal women who drank dairy milk have a small increase in breast cancer risk. (09/04/20)
Read More
Study : Among women with breast cancer, who should have genetic testing for an inherited mutation?
Most relevant for: Women diagnosed with breast cancer who do not know if they have an inherited mutation in a gene linked to breast cancer
Which breast cancer patients should consider genetic testing? Knowing whether you have an inherited mutation may inform the decisions you and your healthcare provider make about treatment. But it can also increase stress and anxiety. This XRAY reviews a study of how different guidelines affect genetic testing recommendations for people with breast cancer. (8/27/20)
Read More