Inherited Mutations and Hereditary Cancer
DNA damage and gene mutations
Genes are made up of . Gene mutations are caused by damage to our . Cells have tools to repair damage. If it cannot be repaired, the body has ways to remove the damaged cell so that it cannot divide and create more damaged cells. This system isn't always perfect, and damage and gene mutations can build up in cells. Over time, this can lead to cancer.
Inherited and acquired mutations
Most genes come in pairs—one copy comes from each parent. Sometimes, a parent may pass a damaged gene with a mutation to one or more of their children. The children with this mutation can pass it to each of their children. A gene mutation that is passed from a parent to their child is called an "." Inherited mutations are damage that are present at birth. Inherited mutations can increase your risk for certain diseases like cancer.
Acquired mutations are those that happen after a person is born and over the course of their lifetime. They are caused by “wear and tear” on genes over time. Some causes of acquired mutations include:
- aging
- exposure to hormones
- exposure to toxins in your environment
- certain viruses
What are hereditary cancers? How are they different from other cancers?
is the name for cancers that are caused by inherited mutations that are can be passed down through generations from parents to their children.
- Cancers in people who have an are called "hereditary" cancers.
- Cancers in people who do not have an are called "sporadic" cancers.
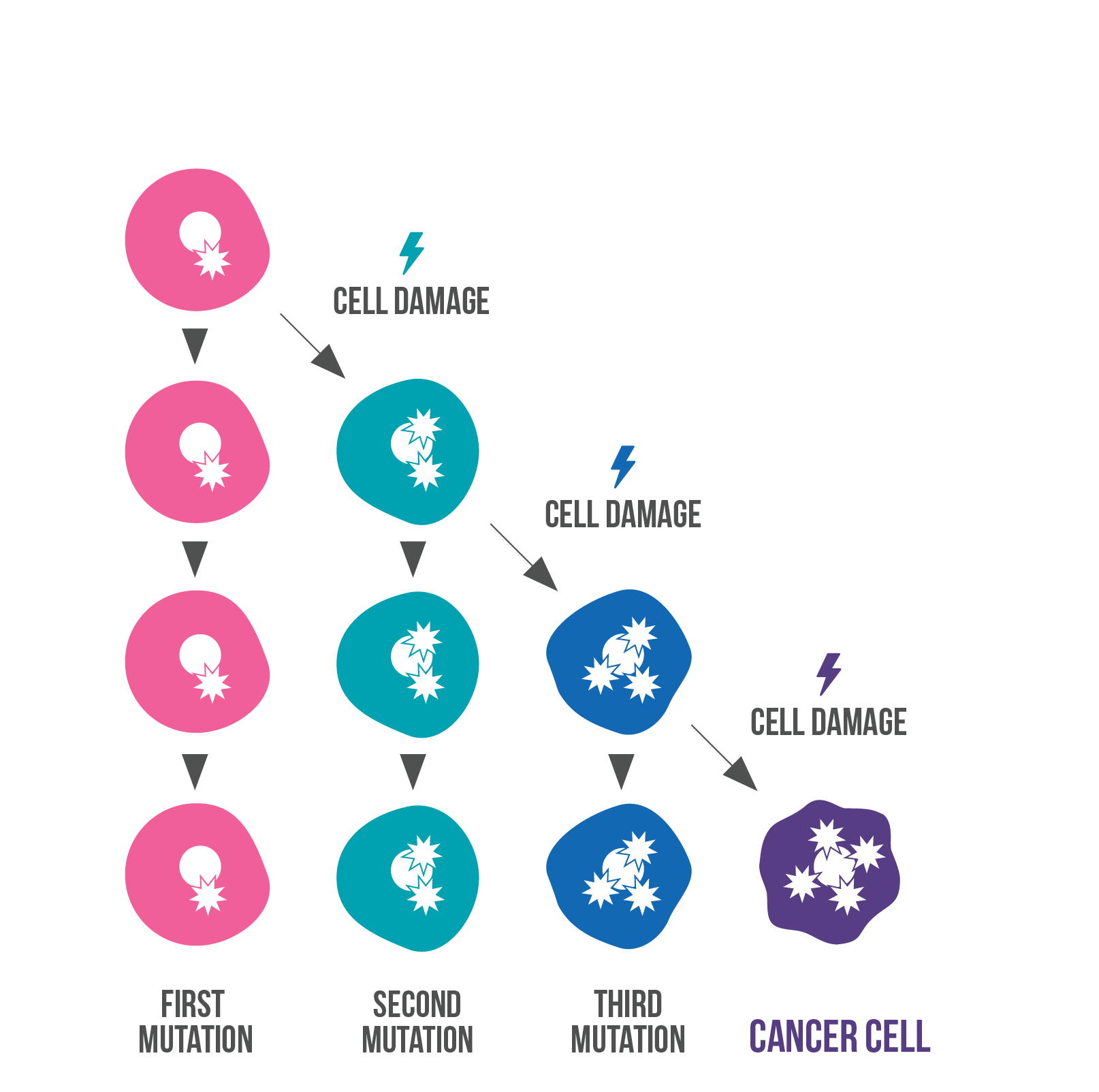
Sporadic cancers are caused by the build up of acquired mutations
With sporadic cancers, normal cells gradually acquire mutations. Over time this can lead to cancer.
When a cell with damaged genes divides, the resulting cells will contain the same mutations. These can acquire additional damage, which is passed on to new cells when the old cells divide. In this way, cell damage can build up over a person's lifetime leading to cancer.
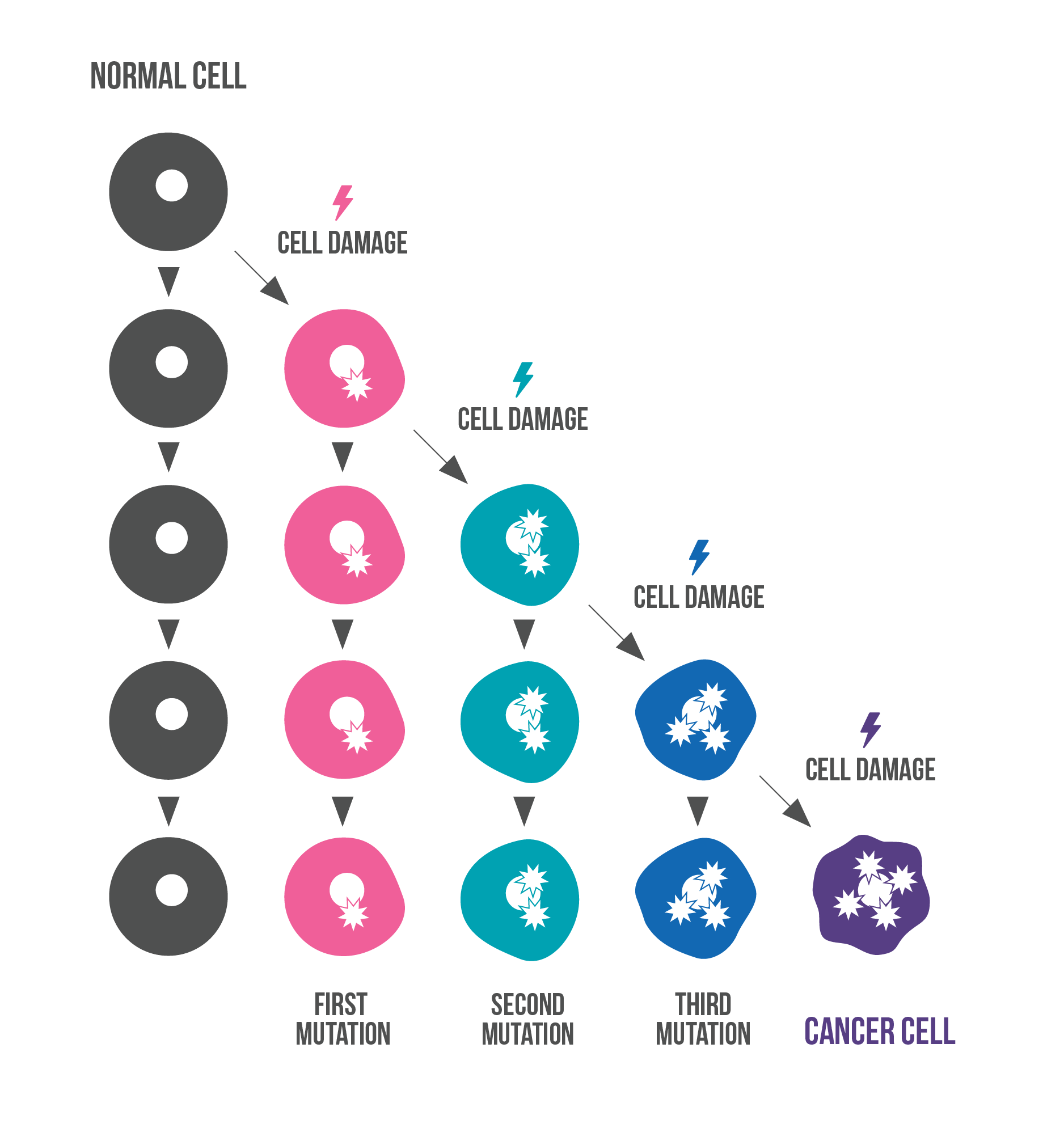
Hereditary cancers are caused by a combination of inherited and acquired mutations
People with inherited mutations are born with one already damaged gene in all of the cells in their body. This means fewer steps are needed for cancer to develop.
Inherited mutations do not always cause cancer. When you inherit a mutation from one parent, you still have a normal copy of the same gene from your other parent. If that normal copy gets damaged, the cell has a harder time repairing further damage. Additional, acquired mutations can build up over time, leading to cancer.
What are damage repair genes?
Certain genes are important for repairing damage. These genes are sometimes referred to as " damage repair" or "DDR" genes.
- In normal cells, mutations in damage repair genes increase the chance that the cell will become cancer. This is why inherited mutations in genes that repair damage increase the risk for cancer.
- In cells that are already cancerous, mutations in damage repair genes can keep the cells from repairing damage caused by treatment. This means that cancer cells with mutations in these genes may be more sensitive to certain treatments.
How are mutations inherited?
People can pass an inherited gene mutation to their children through their sperm or eggs. When a person with a gene mutation has children, each child has a 50 percent chance of inheriting the same mutation.
Mapping your family medical history
Genetics experts look carefully at a family’s medical history for signs of . You can assist them by gathering medical information from relatives on both sides of your family going back as far as three or more generations if possible. They will use this information to create a diagram of your family tree known as a pedigree. This allows them to look for patterns that may indicate an and determine which relatives are at increased risk for cancer.
“Degree of relatedness” is a term used by experts to describe how closely related one family member is to another. "First-degree relatives” share half of their . If a person has an , each of their first degree relatives has a 50 percent chance of testing positive for the same mutation. Second-degree relatives share one fourth of their , third-degree relatives share one eigth of their , and so on.
|
Degree |
Relative |
% of shared |
|
First-degree relatives |
Siblings |
50% |
|
Parents |
50% |
|
|
Children |
50% |
|
|
Second-degree relatives |
Half-siblings |
25% |
|
Grandparents |
25% |
|
|
Grandchildren |
25% |
|
|
Aunts |
25% |
|
|
Uncles |
25% |
|
|
Nieces and nephews |
25% |
|
|
Third-degree relatives |
Cousins |
12.5% |
|
Great grandparents |
12.5% |
|
|
Great-aunts and great-uncles |
12.5% |
More Information on Genes and Cancer
Signs of an Inherited Mutation
These signs may indicate that the cancer in your family is hereditary.
Participate in Genetics Research
Below are some of our featured research studies looking at genetic testing. To search for additional studies, visit our Search and Enroll Tool.
WISDOM Study: Women Informed to Screen Depending on Measures of Risk
Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT02620852
Study for People with Unexpected Genetic Results
Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT02595957
Research Study on the Genetics of Breast Cancer
Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT06773897



